Transforming Energy for America
Renewables
Wind
Wind energy (or wind power) is the process by which wind is used to generate electricity. Wind turbines convert the energy in wind to electricity by rotating the propeller, like blades around a rotor. The rotor turns the drive shaft, which turns an electric generator, known in the industry as Wind Turbine Generator (WTG).
Transformers play a key role in the power transformation of wind energy.
They serve as Generator Step-Up (GSU) to step up the voltages at different stages. All wind generators need a Pad Mount Transformer at its base, or Nacelle, for the first stage step-up and then collectively stepping up on each WTG output feeds a collector Main Power Transformer (MPT) that finally boosts the voltage to connect with the transmission grid. Virginia-Georgia Transformer makes both the liquid-filled pad mount which we catalogue as E2X and the Collector Main Power Transformers (MPT) that are powering several wind farms effectively. The pad mounts are custom designed and built to suit the unique onerous dynamic and harmonic loads of the wind energy generation characteristics and assure against hot spots and gassing.
Power collector transformers right up to 500 MVA / 525 kV serve the sub stations at many wind farms.
Solar
The energy the Earth receives from the sun, primarily as visible light and other forms of electromagnetic radiation, is a powerful source of energy. The technologies that are utilized in this segment are broadly characterized as either passive solar or active solar depending on how they capture and distribute solar energy or convert it into solar power. Active solar techniques include the use of photovoltaic systems, concentrated solar power, and solar water heating to harness the energy. Passive solar techniques include orienting a building to the sun, selecting materials with favorable thermal mass or light-dispersing properties, and designing spaces that naturally circulate air.
A photovoltaic utility-scale power station, also known as a Solar Farm, is a large-scale photovoltaic system (PV system) designed for the supply of solar energy into electric power and feeds the electricity grid. They are differentiated from most building-mounted and other decentralized solar power applications because they supply power at the utility level, rather than to a local user or users.
A utility-scale solar field through solar panel arrays harnesses solar energy and, through photovoltaic cells and invertors, generates electricity that needs to be boosted in voltage levels to make them useful for transmission. This is where VTC designs and manufactures to the onerous harmonic loads of the solar energy segment. VTC’s pad mount transformers again catalogued as E2X to serve as Inverter Step-Up (ISU) to step up the voltages from solar panel arrays and collectively feeds a collector power transformer at the substation also known as Main Power Transformer (MPT). Here again, VTC designs and supplies MPTs large power transformers that boost the voltage levels to synchronize with the grid voltages.
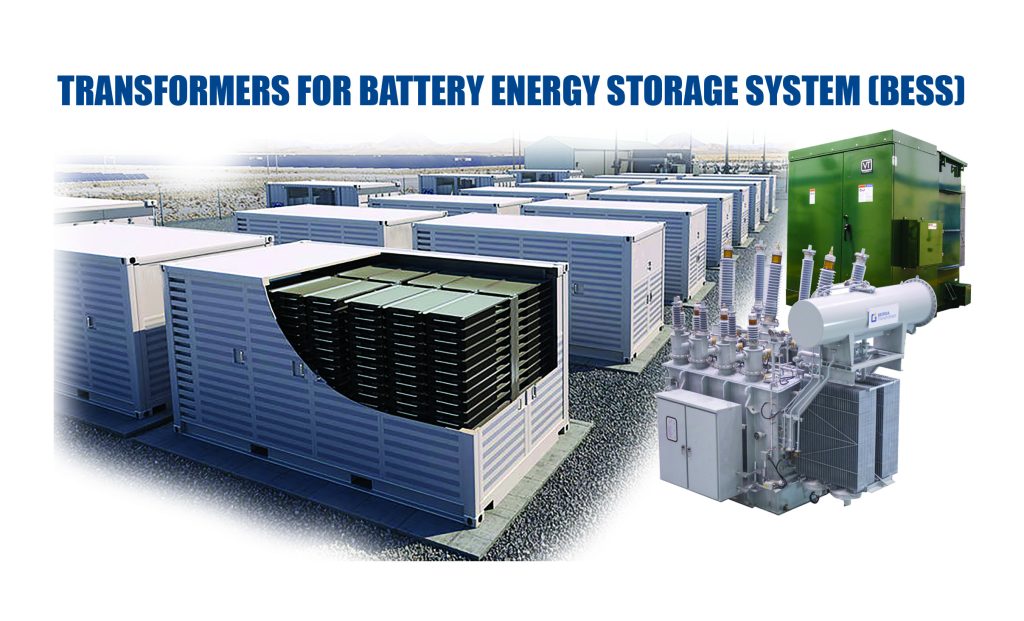
Battery Energy Storage Market And Its Drivers
A Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) is an electrochemical device that collects and stores energy from the grid or a power plant, and then discharges that energy at a later time to provide electricity or other grid services when needed. BESS is a fast-growing market.
Primary drivers for BESS market growth include:- The increase in need for system flexibility due to Wind and Solar projects deployment, along with rapid decrease in the cost of battery technology
- The continuous innovation in BESS and policies to ramp up BESS deployment
- Battery energy storage is one of several technology options that can enhance power system flexibility and enable high levels of renewable energy integration
Virginia Transformer is a market leader in power transformers and has been in business for over 50 years. Our distinguished legacy includes:
- Installed base of over 20,000 transformers
- Technical expertise in providing solutions to renewable power – wind, solar, and battery energy storage – across large and medium main power transformers and padmount
- Leadership in design and manufacturing knowledge and experience for the specific requirements of BESS applications, including special considerations for:
-
-
- Over-voltages
- Inverter applications
- Harmonics profile
- Saturation, power factor
-
-



